Cannabis is all about good vibes and good times, but did you know that a lot of science goes into this powerful plant? It’s important to know the behind-the-scenes action of cannabis so you can make more informed decisions to curate your experience or even target medicinal benefits that can improve your quality of life.
In this blog, we’re going to dive into the science behind cannabis so consumers of any level can elevate their green game.
The Main Components of Cannabis
Firstly, the diverse effects and advantages of cannabis stem from its chemical makeup, which includes cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids:
- Cannabinoids: Cannabinoids are the most prominent components of cannabis, with THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (Cannabidiol) being the most well-known. THC causes the psychoactive effects, or the “high” feeling, while CBD provides therapeutic properties, such as potentially reducing anxiety and pain, without causing psychoactive effects. These might be the most popular, but there are over a hundred different cannabinoids, each contributing to the plant’s overall effects.
- Terpenes: Terpenes are the aromatic compounds in all plants (including cannabis) responsible for their signature scent, from citrusy to piney to spicy to earthy and everything in between. They can also influence the effects of the strain by interacting with cannabinoids in what’s called the entourage effect. Terpenes themselves may also offer benefits like anti-inflammatory or anxiety-reducing properties.
- Flavonoids: Flavonoids are responsible for the pigmentation of the cannabis plant, contributing to its color. They also have potential benefits such as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, and they also partake in the entourage effect, modulating the effects of the strain and enhancing the therapeutic potential.
Cannabis and the Human Body
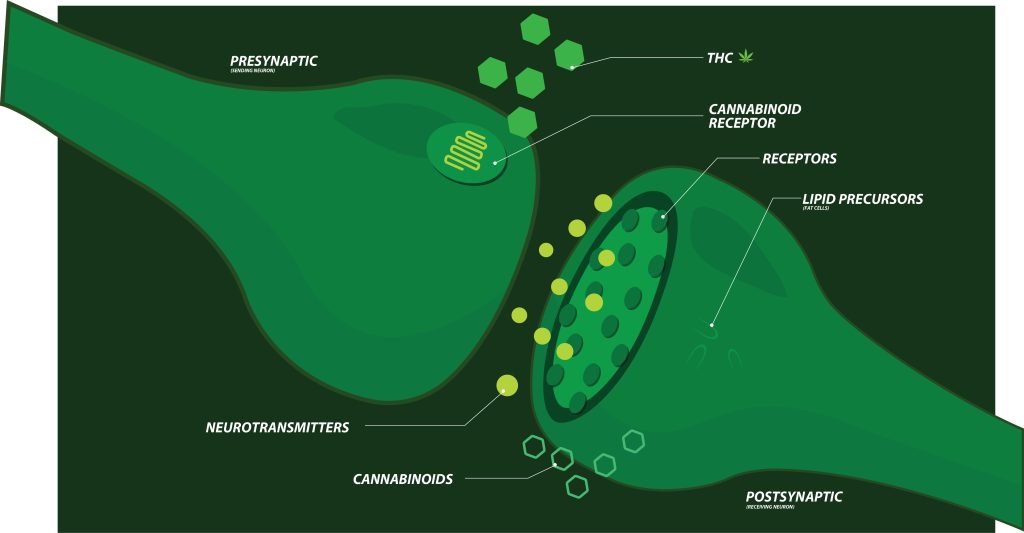
Cannabis has a profound effect on the human body because of the endocannabinoid system (ECS). The ECS exists in everyone regardless of cannabis use and is a crucial biological system that maintains homeostasis, or balance in the body.
Components of the ECS
- Endocannabinoids: These molecules are naturally produced in the body and function similarly to cannabinoids in the cannabis plant. The clever aspect of endocannabinoids lies in their “on-demand” creation, ensuring their use precisely when and where needed.
- Cannabinoid Receptors: There are two main types of receptors, CB1 and CB2, scattered throughout the body. Primarily, you’ll find CB1 receptors in the brain, central nervous system, and other organs. Cells associated with the immune system, especially outside of the central nervous system, more commonly have CB2 receptors. Endocannabinoids can bind to either receptor, and the resulting effects depend on where the receptor is and which endocannabinoids bind to it.
- Enzymes: Enzymes make and break down endocannabinoids after they have been used. These enzymes ensure that the system stays in balance by preventing the use of endocannabinoids for longer than necessary.
Functioning of the ECS
The primary role of the ECS is to keep various physiological and cognitive processes in check. These include pain sensation, mood, appetite, memory, stress response, immune function, sleep, metabolism, and more.
When the ECS detects an imbalance, it produces the appropriate endocannabinoids to interact with receptors. This interaction triggers chemical responses that help balance the system.
Cannabis and the ECS
When consumed, cannabis cannabinoids interact with the ECS similarly to endocannabinoids. For example, THC binds directly to CB1 and CB2 receptors, mimicking the effects of endocannabinoids. CBD doesn’t bind directly to receptors but rather prevents the breakdown of endocannabinoids, allowing them to have a more prolonged effect on the body.
These interactions are what cause the experiences associated with cannabis use, from the high of THC to the therapeutic effects of CBD and other cannabinoids.
The Effects of Cannabinoids on the Body & Mind
The interaction between cannabinoids and the ECS can lead to a wide range of effects on the body and mind, which vary significantly depending on the specific cannabinoid, dosage, and individual physiology.
- Physical Effects: Cannabis can have several physical effects, including pain relief, reduction in inflammation, relaxation of muscles, and alleviation of nausea and vomiting. These effects make it a valuable tool for managing conditions like chronic pain, arthritis, muscle spasticity, and chemotherapy-induced nausea.
- Mental & Emotional Effects: Cannabis can influence mood, stress levels, and anxiety. THC produces euphoria and relaxation but can also increase anxiety or paranoia in some individuals. CBD has a wide recognition for its ability to reduce anxiety and possibly counter some of THC’s psychoactive effects.
- Therapeutic Potential: Beyond the immediate physical and mental effects, the interaction of cannabinoids with the ECS holds significant therapeutic potential for various conditions. Research is ongoing into the use of cannabis and cannabinoids for treating epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, anxiety disorders, and even some forms of cancer, among other conditions.
Why Cannabis Consumption Methods Make a Difference
The way you consume cannabis significantly influences how quickly you feel its effects and how long those effects last. Here’s the skinny:
- Smoking & Vaping: These methods provide quick effects, usually in minutes, lasting 2 to 3 hours. Cannabinoids enter the bloodstream directly through the lungs.
- Edibles: Effects take longer to kick in, 30 min-2 hours, but last longer, 4-8 hours, because cannabinoids are processed in the liver before entering the bloodstream. This processing also makes the effects more intense than with inhalation.
- Tinctures: Tinctures are absorbed under the tongue, so they work faster than edibles, with effects starting in 15 to 30 minutes and lasting about 4 to 6 hours.
- Topicals: Topicals are applied directly to the skin and offer localized relief without psychoactive effects. The onset and duration can vary widely.
In addition to consumption methods, factors like metabolism, tolerance, and product potency play a huge role in the onset and duration of effects.
Shore House Canna – Premier Jersey Shore Dispensary: Empowering You With Canna-Knowledge
As we’ve explored the science behind cannabis, it’s clear that education is the best way to maximize the benefits and minimize the risks associated with cannabis use. At Shore House Canna, we want to empower you with the knowledge to make informed choices.
We encourage you to continue your cannabis journey by visiting our education page. Let Shore House Canna be your guide to enter (or re-enter) the world of cannabis with confidence and clarity.
As Shore House Canna always says: Start with Low and Slow!
*The contents of this blog are intended for informational purposes only. Always seek the advice of a physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.*